이미지 확대

[Courtesy of LG Chem]
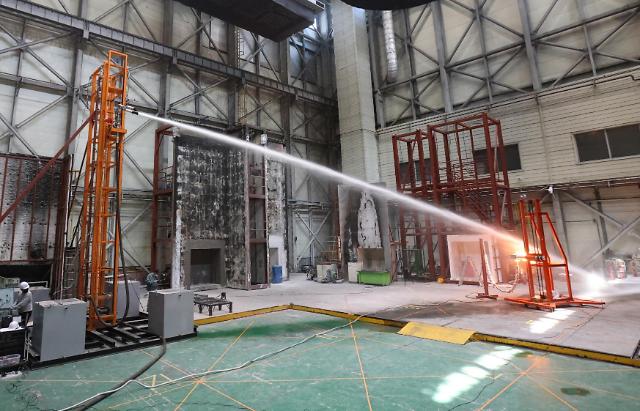
SEOUL -- LG Chem, a chemical unit of South Korea's LG Group, partnered with GS EPS, a private power generation company, to collaborate on a biomass-based eco-friendly energy project, starting the potential establishment of a joint venture for the construction of a biomass power plant by 2025 to produce industrial steam and electricity with waste woods.
Biomass is a plant-based material including agricultural crop residues, algae, and industrial wastes. Wood pellets are the most common type of pellet fuel and are generally made from compacted sawdust and related industrial wastes. Other industrial waste sources include empty fruit bunches, palm kernel shells, coconut shells, and treetops and branches discarded during logging operations.
LG Chem said it has signed a letter of intent with GS EPS to review business strategies toward constructing a joint biomass power plant at the southern industrial port of Yeosu to produce industrial steam and electricity with waste woods by 2025. Should the joint venture be established, LG Chem said it can produce steam from biomass to run its petrochemical operations in Yeosu.
LG Chem described the agreement as a key component of its strategy to ensure a more sustainable future. "Accelerating Net Zero transition across all aspect of the corporate value chain will enable us to more quickly establish a circular economy utilizing renewable and sustainable fuels," LG Chem’s petrochemical business head Noh Kug-lae said in a statement on June 13.
GS EPS operates South Kora's first biomass power plants. "Leveraging GS EPS’ core competencies in renewable energy such as biomass power, we will work closely with partners such as LG Chem to help them achieve their commitment toward Net Zero," said GS EPS CEO Chung Chan-soo.
The two companies would cooperate on the establishment of a power purchase agreement (PPA) for renewable energy in collaboration with Korea Power Exchange (KPX), a state agency responsible for operating South Korea's electricity market and electric power system.
The Seoul government has encouraged companies to adopt clean energy, as part of efforts to achieve zero-carbon by 2050. in April 2022, LG Chem and the state-run Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) opened a laboratory that will focus on the utilization of carbon dioxide in the electrochemical production of ethylene and the biological production of organic acid using biomass and by-product gases.
KIST has developed the core technology for the transformation of biomass into organic acid mainly used for the antimicrobial management of foods and beverages. Biomass can be transformed into valuable organic acids.
Copyright ⓒ Aju Press All rights reserved.



View more comments