[Courtesy of UNIST]
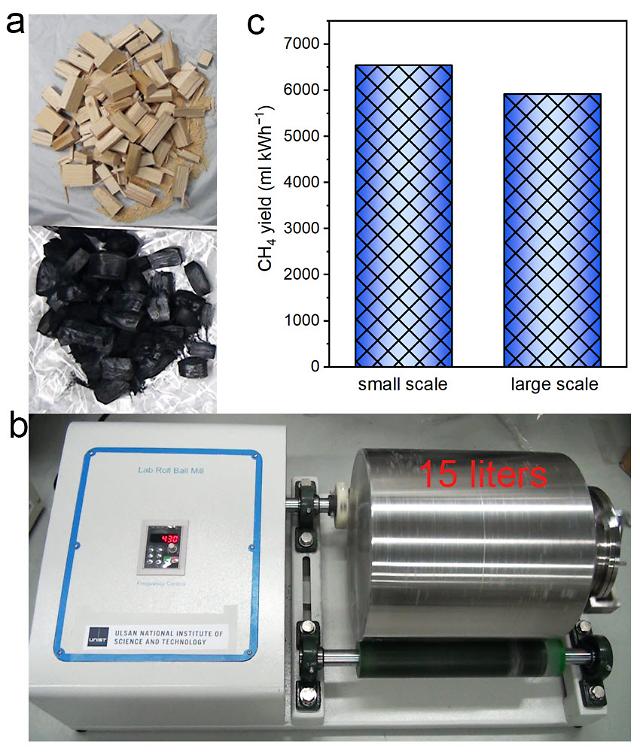
Ball-milling is a method that uses thousands of small metal balls and catalytic materials inside a tubular container. The method uses lateral force created by balls spinning inside the container. When balls crash into carbon-based source materials, carbon nanotubes are transformed into smaller nanoparticles.
The Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) said that its research team has used self-produced wood charcoal to produce methane. Researchers found that when carbon atom bonds break during the ball-milling process, four hydrogen atoms will stick to a carbon atom to become methane.
Using the new methane production technique, researchers were able to acquire a 99.8 percent saturated methane content at ordinary ground-level air pressure, the institute said, adding that conventional charcoal-methane production was carried out in an environment that is hotter than 600 degrees Celsius (1,112 degrees Fahrenheit) to achieve a saturated content percentage of about 80 percent.
"Using the collision power created by the ball-milling technique, we can break down charcoal to produce methane. We think that the technique can also be used to produce methane from coal which is similar to charcoal," UNIST researcher Baek Jong-beom said in a statement on March 14.
Copyright ⓒ Aju Press All rights reserved.