[Courtesy of KIST]
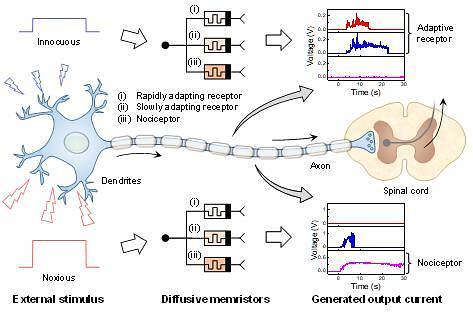
Sensations are signals sent by sensory receptors to the brain to feel the environment around a person. When the environment is too hot, cold, or hostile enough to apply external force onto the body, receptors start to continuously send strong signals to alert the brain. The waves of strong signals are called pain. When a person feels pain, he or she will take action to ease the pain by avoiding such an environment.
It is possible for digital sensors that mimic the human nerve system to detect changes in the nearby environment and measure sensations but many sensor devices cannot decide whether incoming sensations indicate that the device is in a dangerous situation.
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) said in a statement on February 13 that its research team has developed a smart sensory receptor device that can detect dangerous sensations and feel pain. The receptor devices use memristors based on the surface migration of silver (Ag) on silicon dioxide (SiO2) nanorods (NRs). The surface-dominated diffusive memristor allows the direct emulation of biological receptors. A memristor is a non-linear two-terminal electrical component capable of memorizing the direction of the electrical current and voltage even when the power is cut.
"This research holds a great meaning we have succeeded in having a device quickly adapt to weak, anodyne sensations while feel pain to strong and harmful sensations," KIST head researcher Kang Chong-yun was quoted as saying.
According to KIST, the smart sensory receptor device will contribute to the development of artificial skin, artificial organs and humanoid robots. The research was published through the February 2 2022 issue of Advanced Science, a global online science journal.
Copyright ⓒ Aju Press All rights reserved.





View more comments