[Courtesy of KIMM]
A liposome is a spherical vesicle, a cell structure in which liquid or cytoplasm is enclosed by a lipid layer. The liposome is a multi-role player that can work as a drug delivery vehicle for nutrients and pharmaceutical drugs including lipid nanoparticles in mRNA and DNA vaccines.
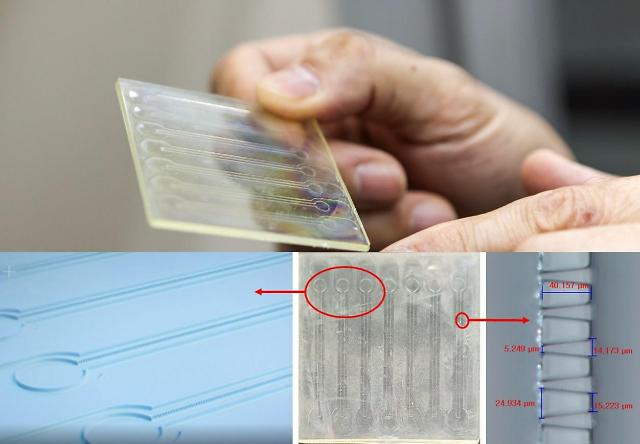
A microfluidic chip is a lab-on-a-chip device that has tens of thousands of microchannels that can control the flow of fluids and create very small uniformly shaped products that are tens of nanometers in size. The microfluidic chip is used in the production of nanoparticles and high-precision pharmaceutical products.
The Korea Institute of Machinery & Materials (KIMM) said in a statement on September 16 that the institute has developed the mass-production technology for microfluidic chips and liposomes. The technology was transferred to Neo Nanotech, KIMM's venture company, for commercialization.
The new technology enables manufacturers to produce microfluidic chips using a plastic material. Molding and packaging technology was also developed to accelerate commercialization. Lipid droplets mixed in an aqueous solution are passed through the chip's 10,000 nano-sized channels to create uniformly shaped liposomes.
"The newly developed technology will contribute to the mass production of uniform lipid nanoparticles, which are key raw materials for next-generation pharmaceuticals including vaccines, as well as functional foods and cosmetics," KIMM's principal researcher Yoo Yeong-eun was quoted as saying.
Copyright ⓒ Aju Press All rights reserved.




